Water movement on surfaces makes more electric charge than expected
Researchers from RMIT University and the University of Melbourne have discovered that water generates an electrical charge up to 10 times greater than previously understood when it moves across a surface.
Time to count plastics in climate action and counter Trump effect
Scientists from RMIT University are calling for countries to include carbon emissions from plastic production and waste in their climate action plans before the upcoming United Nations Climate Change Conference of the Parties (COP 30) in Brazil.
New sat-nav tech boosted by Australia-India collaboration
A satellite navigation system incorporating light-based microchip technology is being scaled up for low Earth orbit applications through a new Australia-India collaboration.
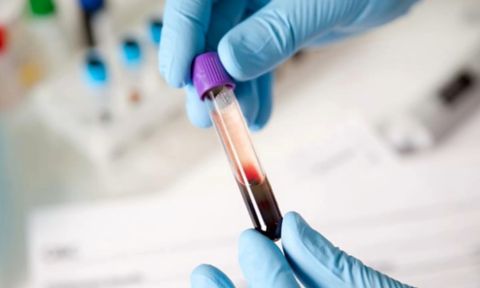
Blood test could make cancer treatments safer and more effective
Scientists from RMIT University and the Doherty Institute have developed a new blood test that could screen cancer patients to help make their treatment safer and more effective.
Warming temperatures may shrink wetland carbon sinks
A major global study using teabags as a measuring device shows warming temperatures may reduce the amount of carbon stored in wetlands.
Gold beats platinum for chemo drugs in new lab study
Gold-based drugs can slow tumour growth in animals by 82% and target cancers more selectively than standard chemotherapy drugs, according to new research out of RMIT University.
Confinement may affect how we smell and feel about food
New research from RMIT University found confined and isolating environments changed the way people smelled and responded emotionally to certain food aromas.
Scientists say plastic rubbish on beaches can now be seen from space
Aussie researchers have developed a new method for spotting plastic rubbish on our beaches and successfully field tested it on a remote stretch of coastline.
Static electricity could help run air conditioners
An invention made from waste polystyrene that generates static electricity from motion and wind could lower power usage by recycling waste energy in air conditioners and other applications.
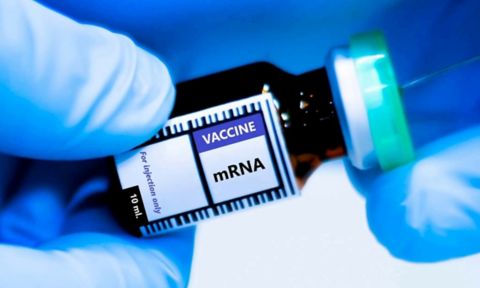
Study may help boost performance and reduce side effects of mRNA vaccines
A study led by researchers from RMIT University and the Doherty Institute has provided the first detailed analysis of how mRNA vaccines circulate and break down in the human bloodstream.
A new pandemic could ride in on animals we eat, researchers warn
Researchers warn the animals we eat could be the gateway for a pandemic in the form of antimicrobial resistance, unleashing a wave of deadly superbugs.
Silicon spikes take out 96% of virus particles
An international research team led by RMIT University has designed and manufactured a virus-killing surface that could help control disease spread in hospitals, labs and other high-risk environments.